FDA Warns of Severe Itching After Stopping Common Allergy Medications
Some patients have reported intense, widespread itching within days of stopping allergy meds such as Zyrtec and Xyzal, prompting an FDA warning.
By
Lana Pine
| Published on May 20, 2025
3 min read
Credit: Adobe Stock/Orawan
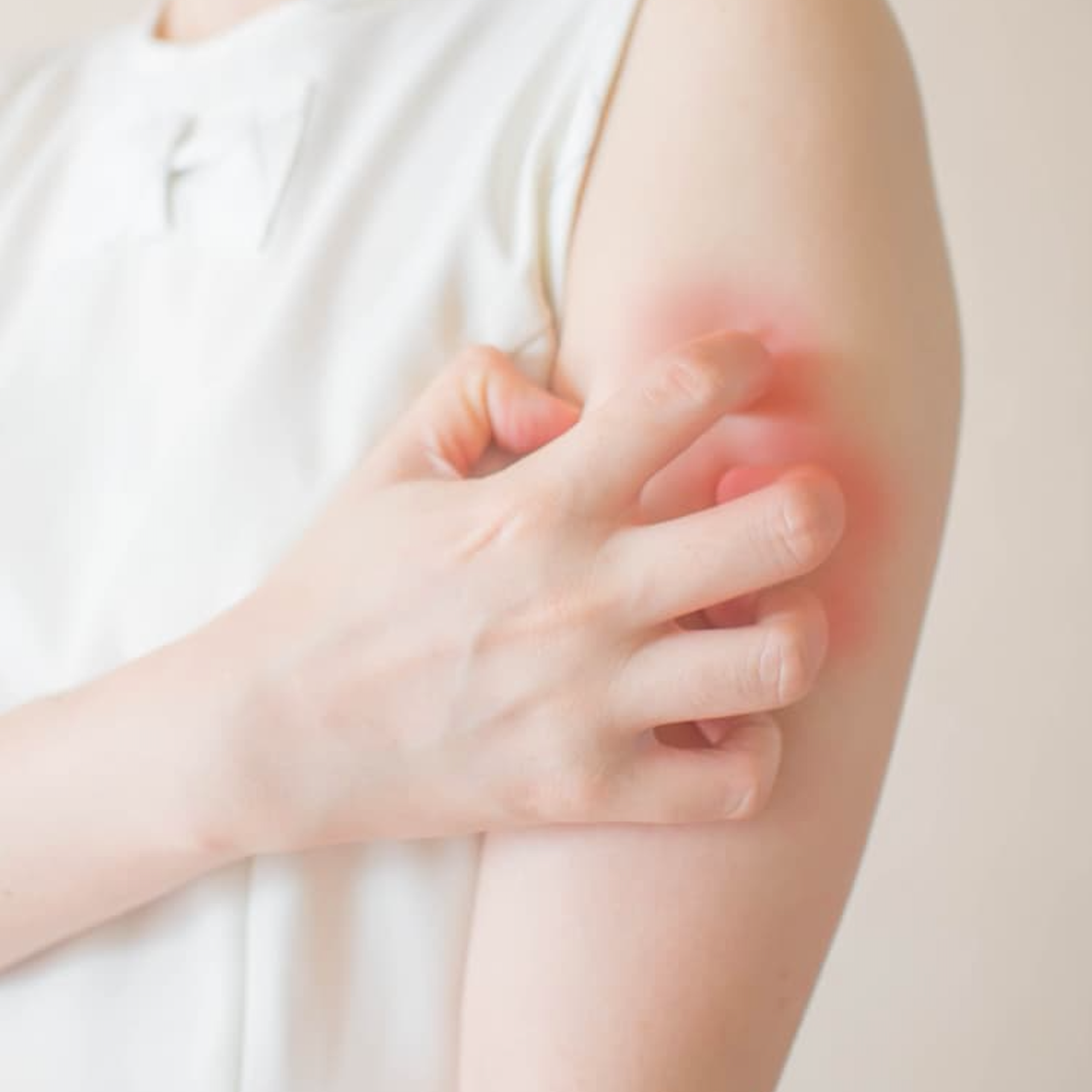
If you take Zyrtec (cetirizine) or Xyzal (levocetirizine) regularly to manage allergies, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) wants you to be aware of a newly identified risk: stopping these medications after long-term use may cause severe, widespread itching, even in people who never experienced itching before.
This rare side effect — called pruritus — has been reported in patients who used these antihistamines daily for several months or even years. The itching often began within a few days of stopping the medication, and in some cases, it was intense enough to interfere with daily life and require medical treatment.
What Are Cetirizine and Levocetirizine?
Cetirizine (brand name Zyrtec) and levocetirizine (brand name Xyzal) are nondrowsy antihistamines commonly used to treat:
- Seasonal allergies
- Year-round allergies
- Chronic hives
They are available over the counter (OTC) and by prescription, and are generally considered safe and effective. However, as with any medication, long-term use may come with risks.
What Is the New Concern?
Between 2017 and 2023, the FDA received more than 200 reports of people developing severe itching after they stopped using cetirizine or levocetirizine. Most of these patients had been taking the medications for more than three months, though a few cases occurred after shorter use. The median time to symptom onset was just 2 days after stopping.
While pruritus after stopping these medications is rare, the reported symptoms were often severe and long-lasting. Some patients described the itching as so intense it left them unable to function, bedridden or struggling with mental health.
What Should You Do?
- Don’t stop abruptly: If you've been taking cetirizine or levocetirizine regularly for months or years, talk to your doctor before discontinuing. A gradual tapering strategy may help reduce symptoms.
- Be alert for symptoms: If you notice intense itching within a few days of stopping either medication, reach out to your health care provider right away.
- Know it may be reversible: In many cases, restarting the medication relieved the itching, and tapering off slowly afterward helped resolve the issue for some.
FDA’s Next Steps
The FDA is updating prescribing information for both medications and is asking manufacturers to add warnings to the Drug Facts labels on OTC versions. The goal is to raise awareness among both doctors and patients about this rare but serious side effect.
While cetirizine and levocetirizine remain safe and effective for many people, it’s important to be aware of the potential for severe itching after stopping long-term use. Always discuss any changes in your medication routine with a health care professional — and report side effects to the FDA’s MedWatch program.

